Processing Scan Data with Ground Control Points (GCPs)
This workflow outlines how to process scan data using Ground Control Points (GCPs) in Emesent Aura.
-
Automatic Match Targets: Circular reflective targets that Aura can match automatically to the imported Survey Data.
-
User Selected Targets: Other identifiable features such as checkerboards, paint marks, or natural landmarks that can be user assigned.
-
Check Points: Surveyed points that are used for independent accuracy validation.
All surveyed points can contribute to georeferencing the point cloud, improving accuracy and reducing Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) drift.
Video Guides
User Selected Targets and Check Point Workflow in Aura
Emesent Automated Ground Control Points Workflow in Aura
Requirements
The following are required to complete this workflow:
-
Software: Aura 2.0 or later.
-
Scan data: Hovermap scan data with visible targets.
-
Surveyed targets: At least 3 GCPs (automatic or user-selected), with optional Check Points.
-
Survey Data: Coordinates for each GCP, including X (easting), Y (northing), Z (elevation), and radius (if using for automatically detected targets).
Procedure
- Step 1: Format Survey Data
- Step 2: Open Emesent Aura
- Step 3: Select Processing Type
- Step 4: Add Scan and Survey Data
- Step 5: Review Loaded Survey Data
- Step 6: Define Output Location
- Step 7: Select Processing Profiles
- Step 8: (Optional) Customize Processing Settings
- Step 9: Start Processing
- Step 10: Open Constellation Matching
- Step 11: Adjust Display Properties (Optional)
- Step 12: Match Survey Points to Targets
- Step 13: Complete Target Assignment
- Step 14: Complete GCP Review
- Step 15: View Final Output
Step 1: Format Survey Data
Prepare a CSV file containing the surveyed coordinates for each GCP target visible in the scan.
Coordinates can be surveyed before or after scanning, but they must be available before processing in Aura to enable georeferencing and improve SLAM accuracy using GCPs. Use a suitable survey instrument such as a GNSS receiver or total station.
Save the file as CSV (Comma Separated Values) only, not CSV UTF-8, or Aura may fail to import it.
2. Enter one line per GCP target using the following structure: ID, X, Y, Z, Radius.
|
Column |
Description |
|---|---|
|
ID |
Unique identifier for the GCP. |
|
X |
Easting coordinate. |
|
Y |
Northing coordinate. |
|
Z |
Elevation. Use a right-handed coordinate system with Z (elevation) defined as up. |
|
Radius |
Target radius in meters. Enter the radius only for flat, circular retro-reflective targets. Leave this field blank for all other target types. Aura only attempts automatic matching when a radius is provided. For Emesent-supplied reflective targets, use 0.125 m for small targets (25 cm diameter) and 0.250 m for large targets (50 cm diameter). |
- Verify column count: Each row must contain exactly 5 columns. Entries with a user-selected target must contain exactly 4 columns.
- Filter entries: Include only the surveyed GCPs that were visible in the scan.
- Save format: Save the file with a .csv extension.
- Close file: After saving, close the file. Leaving it open in Excel may cause issues when importing into Aura.
For easier organization and to avoid errors, it is recommended to store the Survey Data CSV in the same folder as the dataset.
Example
ID,X,Y,Z,Radius
Reflective_big_1,2736.075,5595.273,27.596,0.250
Paintmark1,1326.747,5388.476,22.041,
Reflective_small_1,1309.543,5141.822,29.607,0.125
Reflective_small_2,1787.757,5270.110,21.275,0.125
Checkerboard1,1818.227,5731.992,28.501,
Checkerboard2,2774.159,5115.728,29.817,
Step 2: Open Emesent Aura
1. Open Aura by double-clicking the desktop icon or launching it from the Windows Start menu.
Step 3: Select processing type
1. In the Process tab, click + Process Scan in the upper-left corner of the interface.
2. In the Configure New Scan Job panel at the bottom of the screen, select GCP as the scan type.

Step 4: Add scan and Survey Data
1. In the Configure New Scan Job panel, click Add Dataset to open the Add GCP Data dialog box.
2. In the Add GCP Survey Data popup, add both the dataset folder and the Survey Data CSV.
- Add dataset folder: Browse to the root folder of the unprocessed scan. Do not select subfolders such as Output/. Always choose the root folder of the extracted scan.
-
When prompted, select the Scan Environment. Choose the environment that most closely matches your scan.
- Add Survey Data: Select the CSV file created in Step 1
If you have not yet generated the CSV file, or if the file fails validation, click Download .csv template in the Aura interface to obtain a new template.

Step 5: Review loaded Survey Data
Aura will display the CSV file in the Add GCP Survey Data popup once it has been loaded.
1. Review the data to ensure it is correct and that the correct file has been selected.
2. Choose one of the following options:
-
-
Save – click Save to proceed with processing.
-
Change CSV – click Change CSV to select a different Survey Data file.
-

Step 6: Define output location
- In the Configure New Scan Job panel, locate the Location section at the bottom of the screen.
- In the text box beside the Location scan folder path, enter a descriptive name for the output folder.
- 3. Verify that both the location and the folder name are correct before continuing.
If no name is entered, Aura creates a subfolder named output by default.

Step 7: Select processing profiles
-
In the Configure New Scan Job panel, select a processing profile for SLAM and a processing profile for GCP.
-
The SLAM profile controls how SLAM data is processed.
-
The GCP profile controls the settings applied to GCP processing.
-
For most scenarios, select Standard.
-

On addition of a dataset, profiles may be automatically set based on the hardware used to capture the scan.
If the processed output shows ghosting, misalignment, or duplicated features, select an alternate SLAM profile. If Aura does not automatically detect the expected targets or meet accuracy requirements, select an alternate GCP profile. These profiles affect SLAM and GCP settings, respectively, and should be chosen to suit the scanning environment and mission requirements.
Step 8: (Optional) Customize processing settings
Aura provides several processing settings that can be adjusted when the default profiles are not suitable for the scanning environment or project requirements. These settings are grouped into three tabs: General, GCP, and Output.
1. In the Configure New Scan Job panel, click Processing Settings in the lower-left corner.

2. Adjust the General and Output tabs as needed, using the same options as standard scan processing.
-png.png?width=500&height=62&name=f2f98774-62c1-4ab8-9e74-d4bc9dbd063c%20(1)-png.png)
3. Open the GCP tab to refine how targets are detected and processed. See the GCP settings reference below for details on each option.
4. Click Save to apply changes.
For scans with partial or no Automatic Match Targets, ensure Wait for GCP Target Manual Review remains enabled (default setting). If disabled, Aura will skip the manual step and process the point cloud without GCP correction.
GCP settings
The settings below primarily affect how compatible targets are automatically matched. However, target position uncertainty can also impact the accuracy of the processed, georeferenced point cloud.
|
Option |
Description |
Use Case |
|---|---|---|
|
Intensity |
The expected range of intensity values of the retro-reflective targets. ST-X: 250–255 ST/HVM100: 150–255 |
Use when Automatic Match Targets are not being detected as expected. Narrow or widen the range until reflective targets appear within the detection band. Adjust the band based on the reflectivity of your targets. Widening the band allows Aura to identify more targets but may also pick up additional reflective objects such as bollards, signs, or vehicle mirrors. |
|
Number of points |
The minimum number of points required to detect a target. |
Use when auto-detection of targets is inconsistent. Increase the value when false positives are being created in dense scans, as requiring more points reduces the chance of random clutter being flagged as a target. Decrease the value when targets are small or only partially scanned, as this ensures Aura can still identify them with fewer points. Keep in mind that increasing the value will cause sparsely scanned targets to be missed, while decreasing the value will increase the number of false positives. The default value is 25. |
|
Point cloud target noise |
The expected noise or thickness of the LiDAR points on the target. |
Use when targets appear noisy or when clusters of points around a target are unusually thick. Increase the value if targets are not being detected due to excessive noise or if reflective surfaces appear fuzzy in the scan. Decreasing the value makes detection stricter, which can prevent misidentifying clutter as targets. The default value is 0.02 m (20 mm). |
|
Target position uncertainty |
The uncertainty in the position of the surveyed targets. |
Use when SLAM alignment appears over-constrained to the control points or when survey accuracy is uncertain. Increase the value to give Aura more flexibility when fitting the point cloud to Survey Data — for example, if control points have lower confidence or if overfitting causes distortions in the cloud. Decrease the value when survey control points are highly accurate and should strongly constrain the SLAM alignment. The default value is 0.003 m (3 mm). |
Step 9: Start processing
-
Click Start in the Configure New Scan Job panel to begin processing.

The Configure New Scan Job panel will be replaced with the Processing Scan with GCPS panel.
From here you can:
-
-
Monitor the progress bar and elapsed time during processing.
-
Click Retry if processing fails, to restart from the last successful stage.
-
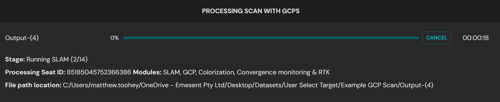
Step 10: Open Constellation Matching
During processing, Aura will automatically detect clusters of points in the scan that resemble circular GCP targets, where a radius has been defined in the Survey Data. If Review GCP is enabled, Aura will then prompt you to review the detected GCP targets.
-
Click Load Constellation to open the intermediate point cloud and the associated constellation file.
-
(Optional) Once the constellation is loaded, you can click Reload Constellation to clear any user changes.

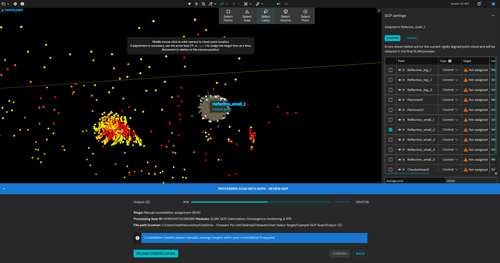
Step 11: Adjust display properties (optional)
To assist in identifying GCP targets in the point cloud, adjust the Color Scale. Intensity is the most effective option, but other scales such as Time or Elevation can also help narrow point selection.

- Change the Color Scale to Intensity to highlight reflective targets.
- Adjust the visibility of points in the scalar filter to display only highly reflective points. This makes GCP targets easier to locate.
- Adjust the scale of the color gradient in the scalar filter to highlight details. Use
alternative Color Scale gradients to help identify targets with variable reflectivity.
Scalar Filter controls
- Adjust the visibility of points: Drag and drop the blue dots along the bottom to set which points in the scale are visible.
- Adjust the scale of the color gradient: Drag and drop the colored square boxes along the top to define which points in the scale correspond to which colors.
Example: Filtering highly reflective targets using the Intensity Color Scale
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Example: Displaying variable reflectivity targets using the Color Scale gradient
In this step, you will link the survey points from the CSV file to their corresponding targets in the point cloud. This establishes the relationship between the surveyed coordinates and the detected features in the scan, which is critical for accurate georeferencing.
If Automatic Match Targets were detected, these will already be assigned. Use this step to confirm the matches and make manual corrections if required. There are two methods for assigning user-selected targets.
Method 1: Manual selection (Recommended)
-
In the Survey Points list, select the survey point you want to associate with the target using the checkbox, then click Add Target. This will automatically open the Select Point tool.
-
Use the Select Point tool to left-click near the center of the target in the point cloud.
-
Refine placement using the keyboard arrow keys.
-
Click Confirm when the target location is correct.
-
Repeat the process until at least 3 survey points are assigned.
Then click Re-Align to align the point cloud with the survey data, making it easier to locate and match the remaining points.
The Re-Align function refreshes the rigid alignment error. Reviewing this value can assist in identifying potential issues such as incorrect point assignments, mismatched targets, or inaccuracies in the CSV coordinates.

Method 2: Auto-select from filtered points (Alternative)
-
Adjust the visibility of points so that only the desired target points remain visible.
-
Use the Select tool to highlight the group of points containing the target.
-
In the Survey Points list, select the survey point you want to associate with the target using the checkbox.
-
Click Add Target. Aura automatically places the target at the center of the selected points.
-
Refine placement with the keyboard arrow keys.
-
Click Confirm when the target location is correct.
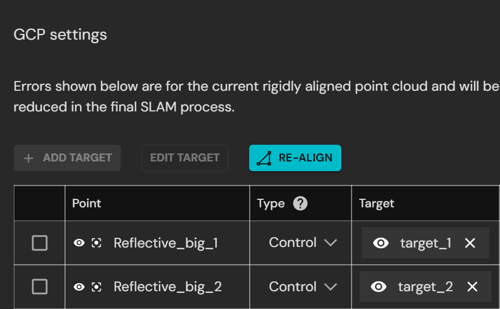
Navigating to and hiding targets
These options can be used to focus on individual targets when reviewing or correcting assignments.
|
Show or hide target: In the Survey Points list, click the eye icon to hide or display the target in the point cloud. |
|
|
Center target: In the Survey Points list, click the center icon to automatically center the viewport on that location. |
Step 13: Complete target assignment
1. Continue assigning the remaining survey points to their corresponding targets in the point cloud.
2. Check the target status in the Survey Points list:
-
-
Green box – the target has been successfully associated with a survey point.
-
Blue box – the target is not associated with a survey point and may need review or deletion.
-
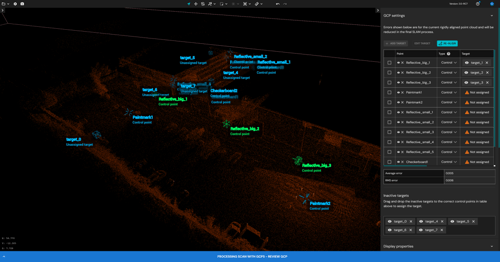
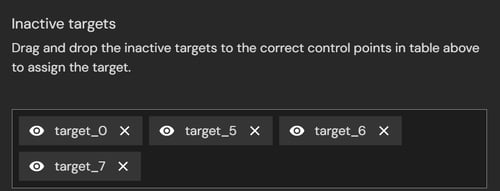
3. Review the list of inactive targets.
These are targets that were not successfully matched to a survey point, or that may have been mismatched to an invalid location. Inactive targets do not contribute to georeferencing or alignment until they are reassigned.
-
-
If valid, drag and drop an inactive target into the Survey Points list to associate it with the Survey Data.
-
Delete the target if it is not valid.
-
Leave unused if the target is not required for georeferencing.
-
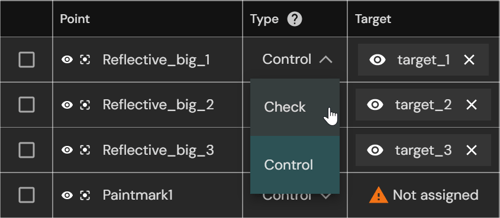
4. (Optional) Mark survey points as Check Points if they should be used only for accuracy validation and not for correcting the scan.
5. Review the pre-SLAM rigid alignment error to confirm accuracy and identify any mismatches.

This step finalizes georeferencing by applying the constellation alignment to correct drift and complete the scan.
1. Confirm all required targets are matched to survey points. Matched points are indicated by a green box and label text.

2. Click Confirm. Aura will then process the scan again with GCPs applied to correct drift.

Step 15: View the final output
Once Aura has completed processing, the Processing with GCPs panel is replaced with the Processing with GCPs Complete panel. From this panel you can access the processed output.
-
Review the final output by either:
-
Opening the files manually from File Explorer, or
-
Using the View function in the Processing with GCPs Complete panel.
-
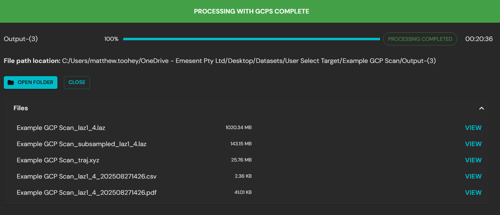
Panel options
-
Open Folder: Opens the scan directory in File Explorer. Inside, you will find the Output folder, or your custom-named folder, containing the processed data.
-
Files list: Each output file includes a View option. Clicking this will open the file in Aura or in the system’s default external program (e.g. PDF viewer or spreadsheet application).
|
File |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Processed point cloud |
Full-resolution point cloud generated from the processed scan. |
|
Subsampled point cloud |
Reduced-resolution version of the processed point cloud. |
|
Scan trajectory |
Trajectory data of the scan path. |
|
CSV accuracy report |
Accuracy report in .csv format, named after the scan with date/time of processing. The accuracy report describes the correlation between ground control points (GCPs) and point cloud data. Each GCP is positioned within the point cloud data, and determines the error in X, Y, and Z. The average error of the individual control points is calculated as a Root Mean Square (RMS). |
|
PDF accuracy report |
Accuracy report in .pdf format, named after the scan with date/time of processing. |



