Filtering Moving Objects
Identifying moving objects within a point cloud is done by estimating statistical scores for points based on their temporal and spatial relationship to their neighborhood. These scores provide a quantitative measure of the likelihood that a point belongs to a moving object, enabling the Moving Object filter to differentiate between dynamic and static elements in the point cloud.
This feature can be applied to your point cloud as a cleaning filter or from the Processing Settings as part of Emesent Aura’s processing workflow.
Using the Moving Object Filter
- Load your point cloud using any of the following options:
- In the top-left menu, click the Project Menu icon then select Open from the popup menu.
- Drag and drop your file directly into the Viewport.
- Go to the Visualize tab then click Add next to the Point Clouds section.
- From the Main Toolbar, click the Cleaning Filters icon then select Moving object filter.

-
Configure the following parameters in the Moving Object Filter dialog box as required.
-
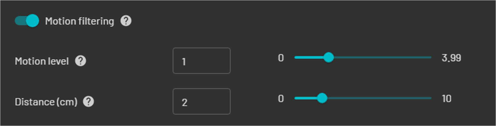
Motion level: Detects movement over 5 second intervals. The higher the value, the fewer moving points are selected.
-
Distance: The maximum distance for recovering fixed points. The higher the value, the more points are retained. A value of 1 to 2 cm is recommended for most scans.

-
-
Under Point outlying, choose whether the outlying points will be deleted or just selected. If you choose Select, the selected points will show in sepia/gray color.

Note: Once the points are selected, running the filter again will require the points to be cleared by pressing the ESC key. The algorithm only takes into account the whole cloud if no points are selected. -
Once satisfied with the selection, press the DELETE key on your keyboard to remove the points.

Applying Motion Filtering from Processing Settings
The filter can also be accessed by enabling Motion filtering from the General tab in Processing Settings. The filter will default to settings based on the profile and detected hardware in the raw scan directory.
-
The filter is disabled by default to avoid accidentally removing some important features with default thresholds including GCP disks if they are not scanned well.
-
An aggressive setting may lead to ‘holes’ on object surfaces in the resulting point cloud.
